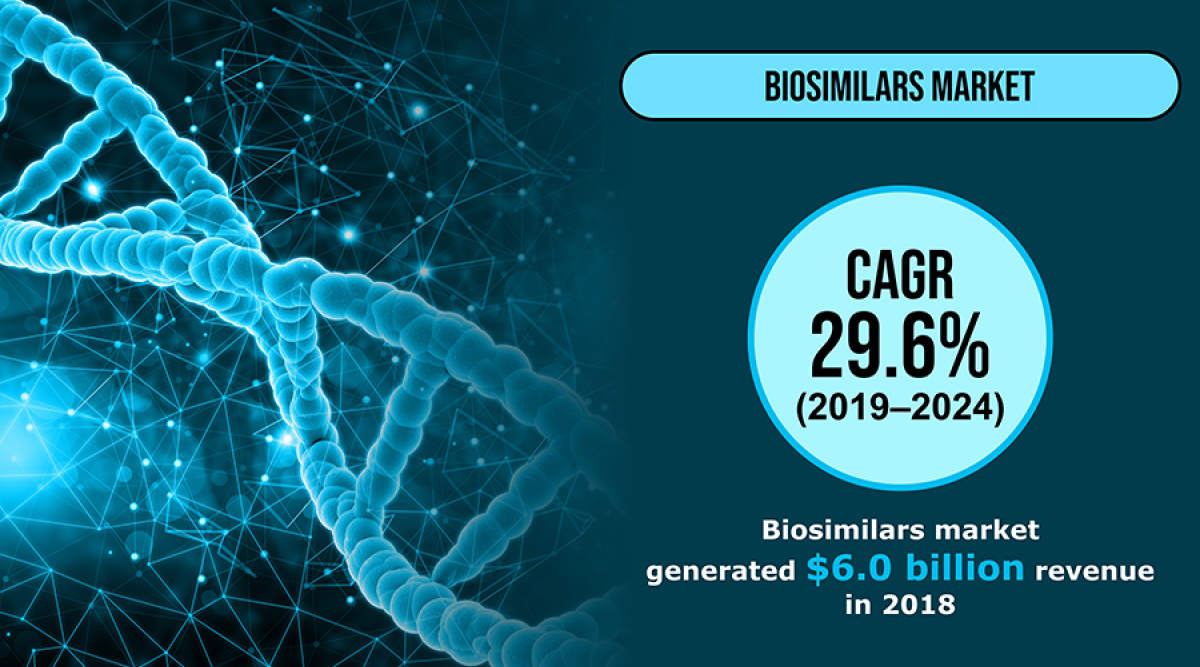
A number of factors such as the increasing incidence of chronic diseases, rising investments in research and development (R&D) initiatives by biopharmaceutical companies, and growing geriatric population will drive the biosimilars market at a robust CAGR, of 29.6%, during the forecast period (2019–2024). Moreover, lower price of biosimilars than reference drugs and presence of an extensive pipeline of these biological products will also catalyze the market growth. The market revenue stood at $6.0 billion in 2018 and it is projected to reach $26.7 billion by 2024.
One of the prime factors contributing to the market growth is the surging incidence of chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) and cancer. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 2.26 million, 2.21 million, 1.93 million, 1.41 million, 1.20 million, and 1.09 million new cases of breast cancer, lung cancer, colon and rectum cancer, prostate cancer, skin (non-melanoma) cancer, and stomach cancer, respectively, will be recorded across the world in 2020. The WHO also estimates that approximately 17.9 million global deaths occur due to CVDs annually.
The product segment of the biosimilars market is classified into recombinant glycosylated proteins, recombinant non-glycosylated proteins, and recombinant peptides. Under this segment, the recombinant glycosylated proteins category generated the highest revenue in 2018, due to the less complexity, high stability, and smooth approval process of such biosimilars. This category is further classified into follitropin, monoclonal antibodies (mAbs), and erythropoietin (EPO). Among these, the mAbs category is expected to hold the largest market share in coming years, due to the surging usage of such biosimilars in treating cancer and diabetes.